C++ lambda function
lambda 문법
기본구조
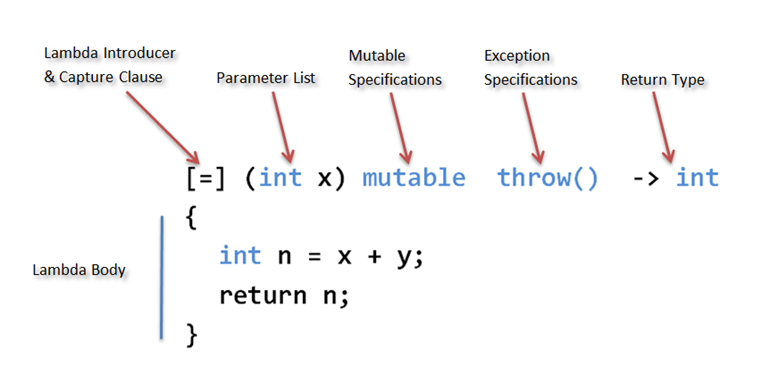
[captures](parameters) -> return type { body }
/*
* captures: comma(,)로 구분된 캡처
* parameters: 함수의 파라미터
* return type: 함수의 반환형
* body: 함수의 몸통
*/
[captures]
| [] | 외부변수를 캡처하지 않음. |
| [=] | 모든 외부변수 복사로 캡처 |
| [=,...] | 모든 외부변수 복사 및 가변인자 템플릿 |
| [&] | 모든 외부변수 참조로 캡처 |
| [&,...] | 모든 외부변수 참조 및 가변인자 템플릿 |
| [this] | 현재 객체를 참조로 캡처 |
[specifier]
| mutable | 복사로 캡처된 변수를 함수안에서 수정할 수 있게 하는 지정자 |
| constexpr | 함수호출 연산자가 상수식(default값) |
lambda를 사용한 sort함수 예제
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_ELEM 10
#define RAND_MAX 100
class Test {
public:
int a;
};
void printElements(vector<Test>& tt) {
for (const auto& v : tt)
{
cout << v.a << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
void insertElements(std::vector<Test>& v) {
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
Test a[MAX_ELEM];
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_ELEM; i++) {
a[i].a = rand() % RAND_MAX + 1;
v.push_back(a[i]);
}
}
int n = 10;
int main() {
vector<Test> testVector;
insertElements(testVector);
int referenceTest = 15;
cout << "정렬 전: ";
printElements(testVector);
// Sort in a ascending order
{
sort(testVector.begin(), testVector.end(),
[=](Test first, Test second) -> bool
{
//n = 0; // =로 정의된 캡쳐블록은 read only.
int a = n;
return first.a < second.a;
});
cout << "정렬 후(오름차순): ";
printElements(testVector);
// Sort in a descending order
sort(testVector.begin(), testVector.end(),
[&](Test& first, Test& second) -> bool
{
n = 10;
referenceTest = 10; // &로 정의된 캡쳐블록은 write 가능
return first.a > second.a;
});
cout << "정렬 후(내림차순): ";
printElements(testVector);
}
return 0;
}